Application of 7T MRI in a Cohort of MRI-Negative Focal Epilepsy: A Pilot Study
Abstract number :
3.248
Submission category :
5. Neuro Imaging / 5A. Structural Imaging
Year :
2019
Submission ID :
2422146
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/9/2019 1:55:12 PM
Published date :
Nov 25, 2019, 12:14 PM
Authors :
Cong Chen, Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine; Juanjuan Xie, Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine; Fang Ding, Second Affilaited Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine; Xinyi Lai
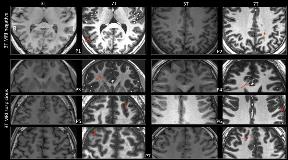
Rationale: To evaluate the diagnostic yield of seven-tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in epilepsy surgical candidates whose 3T MRI results were negative. Methods: Twenty-one patients with pharmacoresistant focal epilepsy were recruited for presurgical evaluation. All patients underwent 3T epilepsy protocol MRI scans (MR750, GE), including high-resolution, three-dimensional (3D) sagittal T1-weighted brain volume imaging (BRAVO). The radiological reports showed no abnormality. After evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including an experienced neuroradiologist, based on detailed electroclinical findings, seven patients among the cohort were found to have an uncertain lesion, and the other 14 patients had normal MRI. All patients underwent high field MRI scans using a 7T Siemens MAGNETOM scanner, including whole-brain 3D MP2RAGE, axial T2 weighted, and axial FLAIR sequences. The 7T images were reviewed by the same multidisciplinary team. Results: After evaluation of 7T images, focal lesions were identified in two (14.3%, in the precuneus and occipital lobe) of the 14 strictly MRI-negative patients; and the uncertain lesions were proved in five out of the seven MRI-suspicious patients (71.4%, 4 patients with lesion in the cingulate, paracingulate, middle frontal, and precentral gyrus separately; another one had double lesions in middle frontal and mesial frontal gyrus). The 7T MR2RAGE sequence exhibited obvious advantages in detecting subtle focal lesions compared to the 3T BRAVO images, such as blurred gray-white matter junction and altered signal intensity. Conclusions: 7T MRI improves the detection of cortical lesion in patients with MRI-negative epilepsy. It help to confirm the epileptogenic lesion in most MRI-suspicious patients and unveiled hidden epileptogenic lesion in a minority of patient who were strictly MRI-negative. It help to guide surgical strategy including implantation of stereotactic electrodes. Funding: National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81671282)