Detection of Subdural Electrode Displacement in Invasive Epilepsy Surgery Workup Using Intraoperative MRI
Abstract number :
1.339
Submission category :
9. Surgery / 9A. Adult
Year :
2018
Submission ID :
502770
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/1/2018 6:00:00 PM
Published date :
Nov 5, 2018, 18:00 PM
Authors :
Bjoern Sommer, Paracelsus-Klinik Osnabrueck; Stefan Rampp, University Hospital Erlangen; Arndt Doerfler, University Hospital Erlangen; Hermann Stefan, University Hospital Erlangen; Hajo Hamer, University Hospital Erlangen; Michael Buchfelder, University H
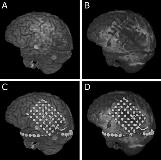
Rationale: Obstacles of electrode implantation in epilepsy surgery include the migration of electrodes in the time span between implantation and the day of explantation. We evaluated a possible electrode displacement using intraoperative MRI (iopMRI) data and CT/MRI reconstruction. Methods: Thirteen patients (9 female, 4 male, median age 26 ± 9.4 years) suffering from drug resistant epilepsy were included in this retrospective study. After implantation, the position of subdural electrodes was evaluated by 3.0 T-MRI and thin-slice CCT for 3D-reconstruction. Localization of electrodes was performed with the volume rendering technique. Post-implantation and pre-explantation 1.5 T-iopMRI scans were coregistered with the 3D-reconstructions to determine the extent of electrode dislocation. Results: Intraoperative MRI at the time of explantation revealed a relevant electrode shift in one patient (8%) of 10 mm. Median electrode displacement was 1.7 ± 2.6 mm with a coregistration error of 1.9 ± 0.7 mm. The median accuracy of the neuronavigation system was 2.2 ± 0.9 mm. Six of twelve patients undergoing resective surgery were seizure free (Engel class 1A, median follow-up 37.5 ± 11.8 months). Regarding postoperative deficits, one patient had a transient paresis of the arm, while permanent deficits including word recognition difficulties, hypesthesia of the left side of the face and a slight hemiparesis occurred in three patients. Conclusions: Comparison of pre-explantation and post-implantation iopMRI scans with CT/MRI data using the volume rendering technique revealed an accurate placement of electrodes. In one patient with a considerable electrode dislocation, the surgical approach was changed due to the detected electrode shift. Funding: No funding
.tmb-.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=aad4b371_0)