THE SIMULATION OF DESMETHYLDIAZEPAM (DMD) CONCENTRATIONS FOLLOWING MISSED DAILY DOSE(S) OF TRANXENE[reg]-SD[trade] and TRANXENE[reg] T-TAB[reg]
Abstract number :
2.224
Submission category :
Year :
2004
Submission ID :
4746
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/2/2004 12:00:00 AM
Published date :
Dec 1, 2004, 06:00 AM
Authors :
1Jennifer R. Riss, 1James C. Cloyd, and 2Stephen D. Collins
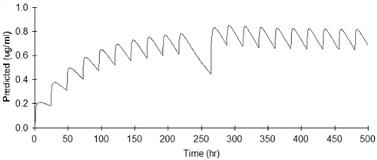
Clorazepate (Tranxene[reg]) is a long-acting benzodiazepine used as an adjunctive treatment for epilepsy. After oral administration, clorazepate is rapidly and completely converted to its active metabolite, desmethyldiazepam (DMD). It is available as two formulations, once daily (Tranxene[reg]-SD[trade]) and immediate release (T-Tab[reg]) tablets. The purpose of this study was to simulate DMD concentrations over time to characterize the effect of missed daily dose(s) [plusmn] replaced doses for both formulations. The following serum concentrations-time profiles were simulated: 1) steady-state (SS) without missed doses, 2) missed daily dose(s) without replacement, and 3) missed daily dose(s) with replacement at the next scheduled dose. Simulations were performed using WinNonLin[reg] (Pharsight Corporation, version 4.0) using a 2-compartment, first order, oral absorption pharmacokinetic model. The dosing schedule was determined from the package insert as follows: Tranxene[reg]-SD[trade] 22.5 mg given once daily and Tranxene[reg] T-Tab[reg] 7.5 mg given every 6 hours for 3 doses. The maintenance regimen was repeated for 20 days to ensure SS conditions. For the T-Tab[reg] and SD[trade] tablets under SS conditions, the times to maximum concentrations were 2.43 and 8.25 hours, the average concentrations were 0.65 and 0.85 [mu]g/ml, and the average trough to peak differences were 0.13 and 0.17 [mu]g/ml, respectively. The impact of a missed day[rsquo]s dose(s) was determined by calculating the difference in peak/trough concentrations at SS vs. the peak/trough concentration after the missed day[rsquo]s dose(s) [plusmn] the replaced dose(s), as well as the percent change in peak and trough differences between SS conditions and missed daily dosing conditions (see Table).[table1][figure1] Despite DMD[rsquo]s long half life ([gt] 48 hours), a missed day[rsquo]s dosing results in altered trough to peak concentrations. The T-Tab[reg] formulation had greater decreases in trough concentrations regardless of dose replacement. After a missed daily dose, the SD[trade] formulation maintains higher trough concentrations, which hypothetically may better prevent breakthrough seizures. (Supported by Ovation Pharmaceuticals, Inc.)